Overview
Otolaryngology in Medical School:
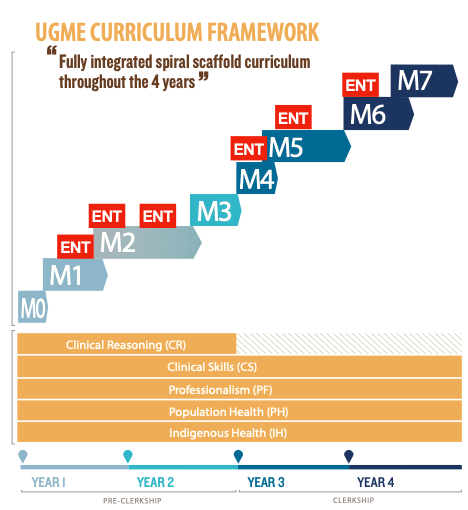
MODULE 1:
In Module 1, students will be introduced to head and neck normal anatomy and will participate in anatomy lab dissections and demonstrations.
MODULE 2:
In Module 2, students will be introduced to more in-depth physiology and disease. Our department provides education on topics in otolaryngology within the Respiratory diseases course (Spring, year 1) and the Neurosciences course (Fall, Year 2). This training is provided in a variety of formats ranging from in person lectures, powerpoint presentations, assigned studies, case-based small group tutorials, and hands on simulation. In the Respiratory course, students will learn topics on hoarseness, airway obstruction, pharyngitis, snoring, sinusitis, epistaxis, and masses of the head and neck. In the Neurosciences course, students will learn about hearing loss, and vertigo. Clinical simulations will teach essential skills for examining the ear, nose, throat and neck and provide practical information for providing patient care.
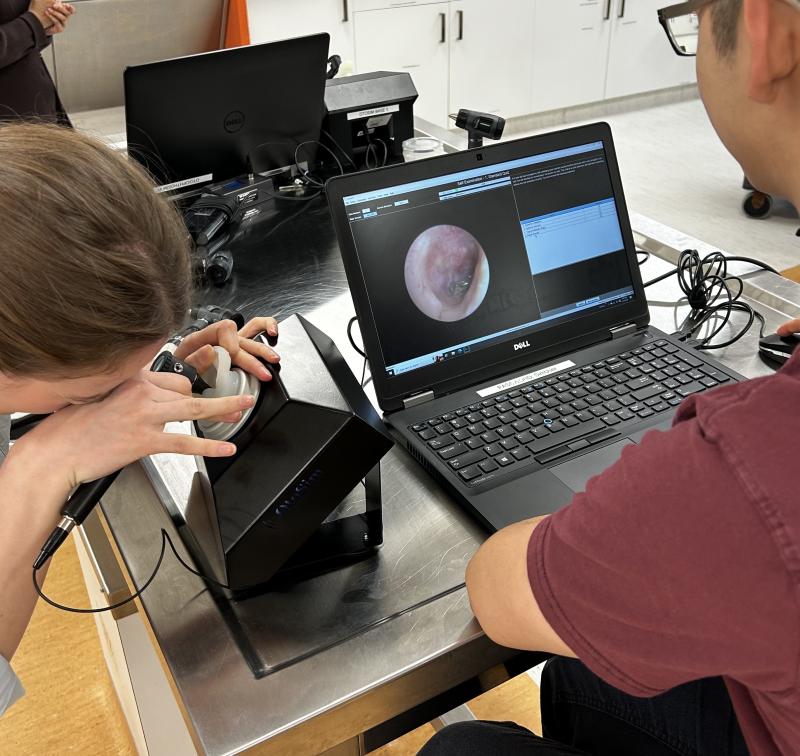

MODULE 4:
Module 4 is designed to help transition the medical student to clerkship rotations and prepare them for patient care. During this module, the Otolaryngology service once again provides hands-on clinical simulation in ear, nose, throat, and neck examinations. These sessions teach the essential skills for examining the ear, nose, throat, and neck, and provide practical information for providing patient care. Students will learn skills in managing epistaxis, flexible nasolaryngoscopy, and fine needle aspiration biopsies of neck masses.
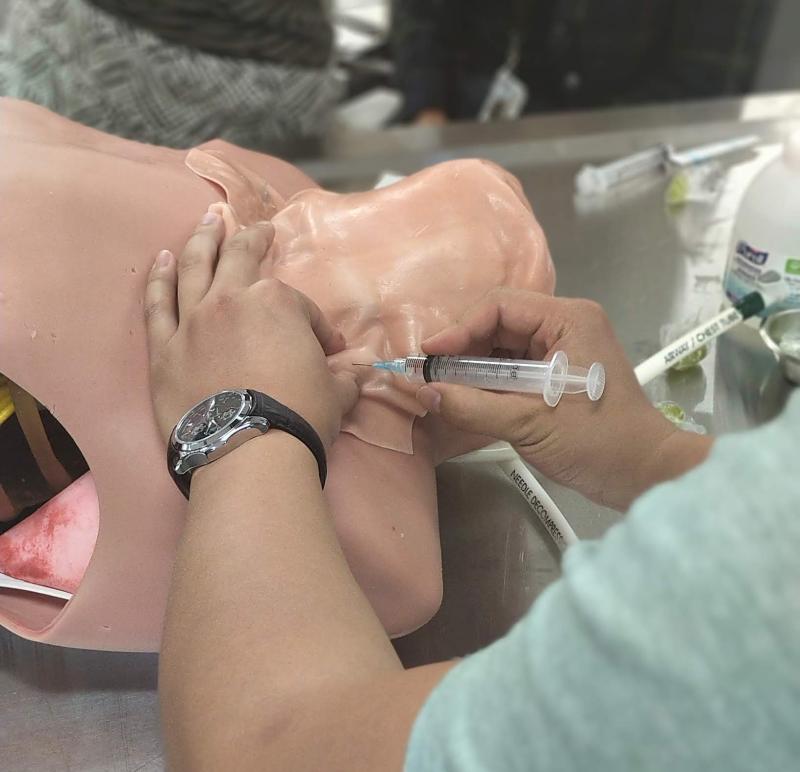
MODULE 5:
Module 5 (Years 3 and 4) represents clerkship training. Rotations in Otolaryngology are offered as a surgical selective opportunity as part of the 6-week Surgery block. Two-week selectives in Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery provide a more comprehensive exposure to head and neck diseases and the broad scope of clinical and surgical cases managed by an otolaryngologist. The rotation is flexible, but in general includes exposures in Otology, Head and Neck Surgery, and Pediatric Otolaryngology. During this rotation, students will participate in managing inpatients, seeing consults from the emergency departments and wards, participate in clinics, and assist in surgical procedures in a variety of settings.
MODULES 6 & 7:
Modules 6 and 7 provide medical students with elective opportunities in various medical and surgical disciplines. Our Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery department provides opportunities for students to expand on the skills they have learned earlier, and further refine their knowledge, skills, and interests in our field. Elective lengths ranging from 2-, 3-, or 4-week durations can be accommodated, depending on the student’s request.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are Otolaryngologists considered surgeons?
Yes!! We are a unique surgical specialty operating in a very complex part of the body. We manage diseases, illnesses, and trauma to the head and neck region with a variety of medical, technological, and surgical approaches.
Do otolaryngologists see adults and children?
Yes! A general otolaryngologist helps treat children and adults, from newborns to the elderly. Some surgeons tailor their practice to treat only children or only adults. Some surgeons complete subspecialty training to manage complex disorders in select populations of children or adults.
How much time do you spend in clinics and in surgery?
The amount of time an otolaryngologist spends in clinics and in surgery can depend on many factors, including subspecialty interests, hospital resources, and how a practice is tailored by the surgeon. In general, we spend about 1 to 2 days operating each week, and 2-3 days in clinics each week. Some subspecialties, such as surgical oncology, may have higher operative volumes. Some subspecialties, such as laryngology and facial plastic surgery, have higher volumes of outpatient clinic-based procedures and procedures done under local anesthetic and IV sedation.
What kinds of activities are performed in clinics?
Our outpatient clinics perform a high volume of procedures that include cerumen debridement, otomicroscopy, nasal endoscopy, flexible nasolaryngoscopy, fine needle aspiration biopsies, nasal cautery, “lump & bump” excisions under local anesthetic, and stroboscopy voice assessments. We also interpret audiograms and vestibular tests to diagnose and treat ear conditions.
When will I get to experience Otolaryngology?
As a medical student, you will get expose to Otolaryngology in your first year studies. You will receive didactic lectures, interactive group sessions, case-based tutorials, and experience ENT clinical skills in action in our simulation courses in the skills lab.